
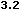

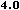

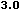

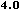


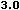

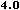

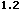

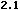

 |
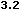  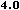  |
 |
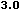  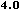  |
 |
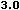  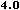  |
 |
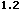  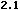  |
This element adds the possibility of programming inside a HTML document by using a scripting language. The functions are programmed inside the SCRIPT container.
This element can be used in the HEAD and BODY section of the document.
To keep older browsers, that do not support scripting, from displaying the source of the scripts it is a common use to comment the contents of the SCRIPT element, like this:
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript">
<!-- Hide contents from older browsers
function ShowMessage(Msg) {
alert(Msg)
}
// End hiding the contents -->
</SCRIPT>
<!ELEMENT SCRIPT - - %Script; -- script statements --> <!ATTLIST SCRIPT charset %Charset; #IMPLIED -- char encoding of linked resource -- type %ContentType; #REQUIRED -- content type of script language -- language CDATA #IMPLIED -- predefined script language name -- src %URI; #IMPLIED -- URI for an external script -- defer (defer) #IMPLIED -- UA may defer execution of script -- >from the HTML 4.0 DTD, "Copyright © World Wide Web Consortium, (Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et en Automatique, Keio University). All Rights Reserved."
 |
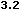  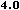  |
 |
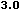  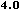  |
 |
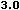  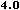  |
 |
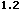  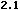  |
 |
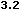  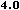  |
 |
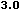  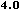  |
 |
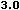  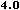  |
 |
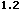  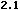  |
document.write() function. That
way the browser knows that the script doesn't influence the initial rendering
of the page, and this may speed up viewing the document.
 |
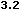  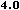  |
 |
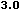  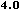  |
 |
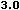  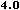  |
 |
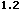  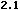  |

With every new version of Netscape Navigator additions are made to the
JavaScript language. This means that not every version has the same scripting
capabilities. To be sure the browser can handle a script there is a way to
specify which version of JavaScript is needed. This is done by a different
value for this attribute.
language="JavaScript" is supported by Navigator 2.0, and
Internet Explorer 3.0, language="JavaScript1.1" is
available in Navigator 3.0 and language="JavaScript1.2"
is available in Navigator 4.0.
If you write a script that uses features of a higher version you can anticipate to browsers that don't support that version. If you include a function with the same name, but in another SCRIPT element, using a different language each browser version will pick the script version it can execute. But you must put the highest version first in the page, followed by older versions. For example:
<HEAD>
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript1.2">
function yourFunction() {
// The version which uses 1.2 features.
}
</SCRIPT>
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript1.1">
function yourFunction() {
// The version which uses 1.1 features.
}
</SCRIPT>
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript">
function yourFunction() {
// The basic version.
}
</SCRIPT>
</HEAD>

 |
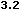  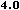  |
 |
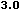  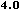  |
 |
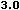  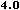  |
 |
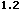  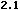  |
 |
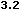  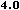  |
 |
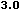  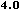  |
 |
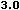  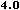  |
 |
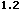  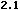  |
This attribute replaces the deprecated language attribute.
<SCRIPT language="JavaScript">
|