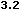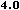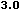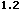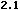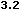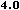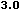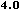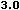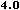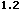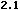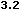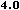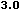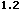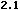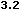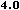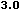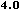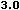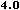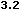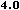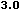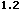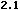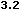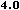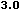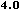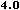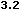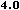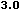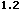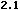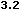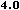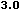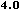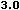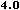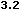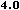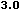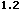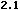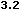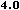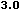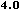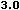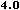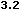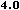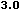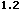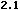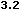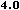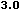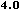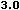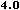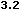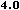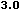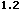<AREA>...[</AREA>]
Used to implement a client-side image map. An image map is an image with one or
more active regions which are hyperlinks to other documents on the world wide
web. The AREA element identifies these active regions, and the documents they
link to.
An image map created this way, with the MAP and AREA elements, is called a
client-side image map because the client, the browser, decides what document a
link will point to.
Another possibility to create an image map is a server-side image map. When the
user clicks on a such a map the coordinates of the mousecursor at the time of
the click are sent to the server. A program on the server processes these
coordinates to a destination link. A server-side image map can be created with
the ISMAP attribute of the IMG element. Also you
must put a file on the server with the regions of the map. The format of such a
file depends on the program processing the map.
Because a client-side image map doesn't use an additional request from the
server to execute the link I would prefer to use this in favor of the
server-side image map. Another advantage is that the browser can act on the
position of the mouse over an active area, to show the address of the link in
the status bar or activate a script.
If two or more AREA's overlap, the region defined first in the map definition
takes precedence over subsequent regions.
The AREA element is only valid inside the MAP
element.
<!ELEMENT AREA - O EMPTY -- client-side image map area -->
<!ATTLIST AREA
%attrs; -- %coreattrs, %i18n, %events --
shape %Shape; rect -- controls interpretation of coords --
coords %Coords; #IMPLIED -- comma separated list of lengths --
href %URI; #IMPLIED -- URI for linked resource --
nohref (nohref) #IMPLIED -- this region has no action --
alt %Text; #REQUIRED -- short description --
tabindex NUMBER #IMPLIED -- position in tabbing order --
accesskey %Character; #IMPLIED -- accessibility key character --
onfocus %Script; #IMPLIED -- the element got the focus --
onblur %Script; #IMPLIED -- the element lost the focus --
>
from the HTML 4.0 DTD,
"Copyright ©
World Wide Web Consortium,
(Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et en Automatique,
Keio University).
All Rights Reserved."
Core attributes:
class
id
style
title
Internationalization attributes:
dir
lang
Events:
onclick
ondblclick
onmousedown
onmouseup
onmouseover
onmousemove
onmouseout
onkeypress
onkeydown
onkeyup
ACCESSKEY
Description of the accesskey attribute
ALT
Provide an alternative for non-graphic browsers for the specific area. This can
give the users of browsers that do not have the ability to show graphics an
alternative way to select the areas of an image-map.
COORDS
The definition of the shape of the active area. The number of coordinates
depends on the shape of the area.
| Shape |
Coordinates |
Explanation |
| CIRCLE |
X,Y,Radius |
Define a circle with X,Y as the center and given radius.
|
| POLY |
X1,Y1,X2,Y2...,Xn,Yn |
Define a polygon with n points, using an X,Y pair for each point of the
polygon.
The polygon is not automatically closed, so include the starting point again
as the last point to close the polygon.
|
| RECT |
Left,Top,Right,Bottom |
Define a rectangle with upper-left corner (Left,Top) and lower-right corner
(Right,Bottom).
|
The upper-left corner of the image is (0,0).
In HTML 3.2 you can supply all the values with a percent sign as a suffix to
let the values be interpreted as percentages of the image's width and height.
HREF
This is the URI to link to when the area in the image is selected.
(see RFC 1630
 for the complete RFC).
for the complete RFC).
An URI consists of the following elements :
<protocol>://<host>:<portnumber><path><anchor>?<parameters>
protocol
- The protocol you want to use. Some well-known protocols are :
| protocol |
Usage |
| http |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol, for World Wide Web pages
|
| ftp |
File Transfer Protocol, for downloading and uploading files
|
| news |
Reading and posting messages to newsgroups
|
| gopher |
Menu like information system, used before the WWW got popular.
|
| telnet |
Remote login on another computer
|
host
- The host computer which has to handle the request. This can be a
four-number internet address, or the name of the computer.
portnumber
- On a computer you can set up more than one server (program) which handle
the same protocol. Each server is assigned its own portnumber to which it
listens. Each protocol has a default portnumber, and most programs add
this if the address does not contain a portnumber. For example the default
portnumber for http is 80.
path
- The directory on the computer where the information is stored.
anchor
- For an HTTP address you can create anchors in a page, which lets you jump
to a specific position in that page. Anchors are created with the NAME
attribute of the A element.
parameters
- If the address links to a program you can supply information to this
program with this parameters. What parameters you can use depends
completely on the program.
If you want to link to an anchor which has been created with the NAME attribute,
Add the character # followed by the name of the anchor to the link. By using
only the #<NAME> syntax as the destination of the link you can link to a
specific position with the current document. This can be used for things like a
table of contents.
NOHREF
Exclude an area from the image-map. This can be very useful when you have
defined a default URL for the complete map by using shape="default" on another
area.
NOTAB
This attribute prevents the browser from reaching this area when the user
repeately uses the Tab key to progress through the page.
ONBLUR
Description of the ONBLUR attribute
ONFOCUS
Description of the ONFOCUS attribute
SHAPE
Defines the shape of the area. Supported values are :
| Value |
Shape |
| DEFAULT |
The areas on the map not covered by a shape. |
| CIRCLE / CIRC |
Circle. |
| POLYGON / POLY |
Polygon. |
| RECTANGLE / RECT |
Rectangle. |
If the SHAPE attribute is omitted shape="rect" is assumed.
TABINDEX
Description of the TABINDEX attribute
TARGET
The TARGET attribute forces the load of that link into the targeted window.
The value supplied with the attribute must be the same as the name of the
window, and is case-sensitive. The name of a window can be assigned if it is
a frame. If a window with the supplied target name does not exist then a new
window will be created with that name.
These names all begin with the underscore character. Any targeted window name
beginning with underscore which is not one of these names, will be ignored.
| Value |
Description |
| _blank |
This target will cause the link to always be loaded in a new blank window.
This window is not named.
|
| _self |
This target causes the link to always load in the same window the anchor was
clicked in. This is useful for overriding a globally assigned BASE target.
|
| _parent |
This target makes the link load in the immediate FRAMESET parent of this
document. This defaults to acting like _self if the document
has no parent.
|
| _top |
This target makes the link load in the full body of the window. This
defaults to acting like _self if the document is already at the
top. It is useful for breaking out of an arbitrarily deep FRAME nesting.
|
 |
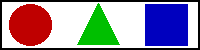
<MAP name="area">
<AREA shape="circle" coords="30,24,21" href="AREA1.html" alt="Circle">
<AREA shape="poly" coords="77,44,119,44,98,3,77,44" href="AREA2.html" alt="Triangle">
<AREA shape="rect" coords="145,4,187,44" href="AREA3.html" alt="Square">
</MAP>
<CENTER><IMG src="AREA1.gif" usemap="#area" border="0" width="200" height="50" alt=""></CENTER>
|
| |
 |
|